1. Relationship between HTML, CSS and JavaScript
Every time you open a new website, you might notice that each of them has their unique layout and you would interact with various web pages differently. The three core languages that
serve as the backbone of a website are HTML, CSS and JavaScript.
To help you gain a better understanding about the relationship between HTML, CSS and JavaScript, a standard two-storey house will be used as an analogy.
Just as its role in constructing a web page, HTML, in this example, is the structure of the house. It, however, would be quite boring if you build a house with a plain white colour
covering the entire place. This is where CSS comes in and adds some style to the house. Similar to how it adds style to a web page, CSS enables you to apply, for instance, greatly
contrast colours for distinct parts of the house as well as add different designs to the living room, kitchen and so on. With CSS styles being implemented, the house now becomes more
appealing and attractive. It should be highlighted that CSS is pointless without HTML as there would be nothing to style. CSS, therefore, has a tight bond with HTML and cannot exist
on its own.
The house is not yet complete as it’s still missing something. And that is the interaction between you and the house, which is where JavaScript offers its ability to create interactive
functionality. Let’s imagine that your house has a facial recognition security built into the house. That means when you arrive at the door, the camera will scan through your face and
trigger the door to be unlocked. Another example of JavaScript’s behaviour is when you turn on a switch and a light comes on or power is delivered. Without JavaScript, you can still live
in your house but will have very limited functions.
From the provided analogy, you can see that just like building a stylish and fully functional house, it’s crucial to develop a nice-looking but also interactive website to generate
seamless user experience. In another word, HTML, CSS and JavaScript cooperate and complement one another to produce an output that is comprised of content, style and interactivity.
2. What are control flow and loops ?
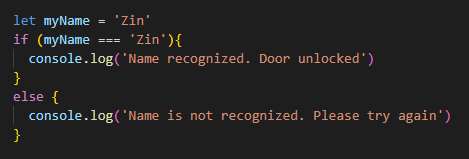
n programming, control flow refers to the order in which statements and functions are executed by the computer. Let’s take a look at the snippet of codes below.
In this example, a conditional structure is used to control the flow of the program. The piece of code inside the “if” statement is executed if the variable ‘myName’ is set to ‘Zin’.
Otherwise, the code located inside “else” is executed. Depending on the value of the variable, different codes will get executed.
Loops are often written in a script, and they have the power of changing the control flow. A loop is a sequence of instructions that get repeated until the specified condition is
achieved. The action of grocery shopping can be used as an example for a loop. When you go to supermarket, you often first look at the first thing on your to-buy list, then walk to the
corresponding aisle where the product is located and grab the product of interest. You will then move on to the next thing on your list and repeat the same cycle again. And you will
keep iterate until all the items on the list are ticked off.
3. What is the DOM and how you might interact with it ?
The Document Object Model (DOM) is a programming interface that defines the structure of HTML documents as well as how it is accessed and manipulated. Within the DOM, all parts of the
document including elements, texts, attributes, etc. are represented as nodes in a tree-like structure.
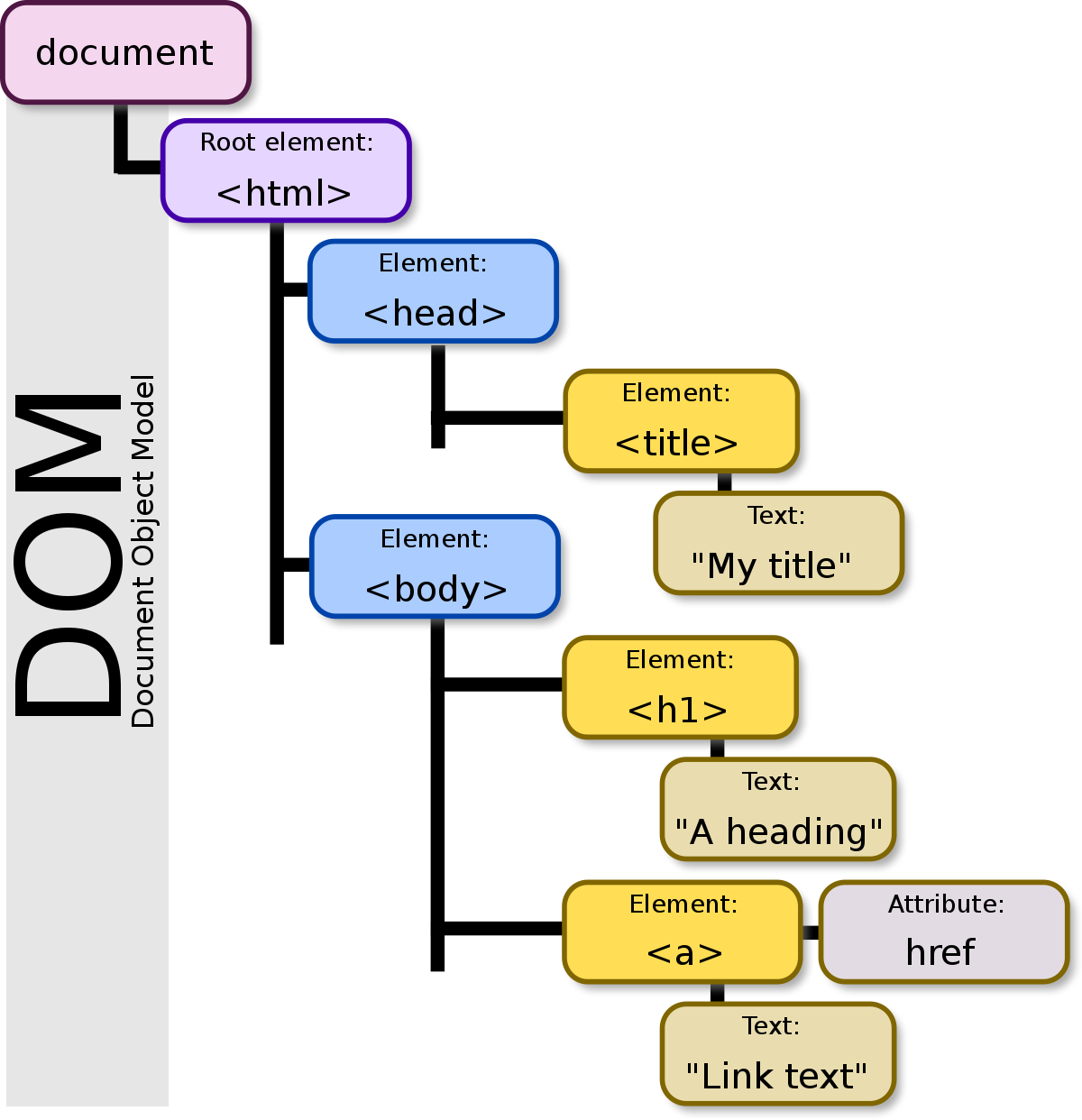
It should be stressed that the DOM is NOT a programming language, but it rather acts as gateway that enables JavaScript to access and modify its elements. Without DOM’s presence, there
would be no layout of webpages for JavaScript to interact with.
There are different ways to access elements in the DOM but the easiest way is to utilize their unique IDs. To do so, you will need to use getElementById() method that is
provided by the DOM.
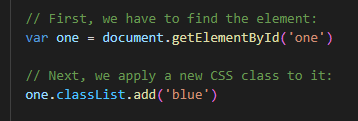
The purpose of the code above is to first locate the element with the id attribute of ‘one’ and then add the class called ‘blue’ to that element.
4. Difference between accessing data from Arrays and Objects
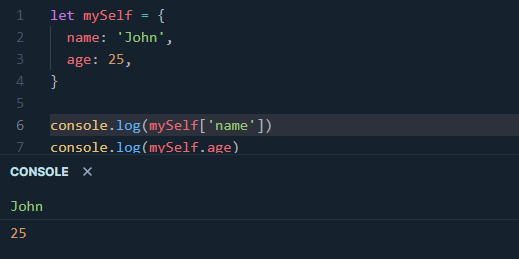
To access data from Objects, you can use either dot or bracket notation. The example below demonstrates that using either way will return the corresponding value of the chosen key.
It should be noted that value and key are the main properties of an object. In the provided example, ‘name’ and ‘age’ are keys while ‘John’ and 25 are their respective values.
With Arrays being used to store a collection of ordered items in a single variable, items can only be accessed via their numerical positions that are placed inside square brackets
[index]. It’s of paramount importance to remember that the very first item in an array starts at an index of 0. The following example will further clarify this point.
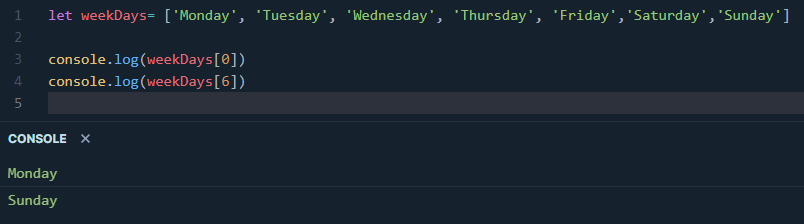
As can be seen, the value at the index of 0 is ‘Monday’ and since it starts at 0, the largest index number is 6 with relative to its size of seven items.
5. What are functions and why they are useful ?
In JavaScript, a function is a block of reusable code written to perform a particular task. Refer to the following code to see how a function is defined and called.
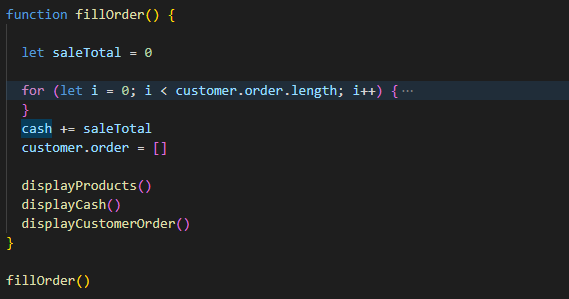
From the example above, you can see that the term ‘function’ keyword is used to declare a function. Also, there are three other functions that appear in yellow are being called within
the fillOrder() function.
Functions are useful in programming owing to their reusable code. Instead of having to repeat identical blocks of code throughout different parts of your program, you only need to write
that code once in the form of a function. When you need to reuse the code to achieve a certain outcome, you can just simply call it to execute the function.